In the latest of our quarterly updates, we use our unique national dataset to provide a comprehensive view of the key trends in Scotland’s independent healthcare sector, covering data up to and including the end of Q2 2025.
The data covers private healthcare in-patient/day-case market activity and includes breakdowns by year for insured cases, ‘self-pay’, Top 10 procedures and demographics.
(Q1 = Jan – Mar; Q2 = Apr – Jun; Q3 = Jul – Sep; Q4 = Oct – Dec)
Private healthcare sector market activity
At a glance
Changes from Q2 2024 to Q2 2025:
- Reported private hospital/clinic admissions were up 3% in Scotland.
- Private medical insurance admissions increased by 3%.
- Self-pay admissions increased by 4%.
- Funding for admissions was 54% insurance and 46% self-pay.
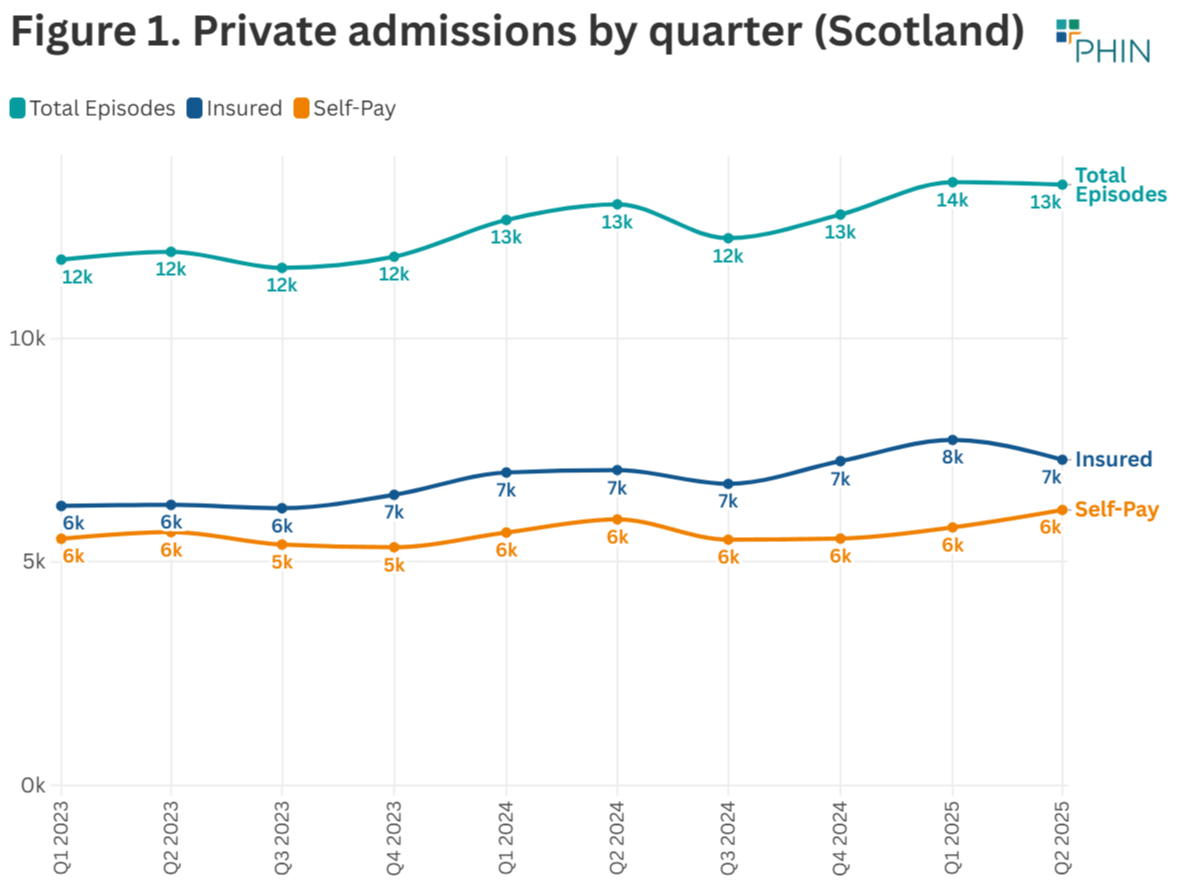
Private healthcare in-patient admissions up in the second quarter of 2025
The total number of admissions in Q2 2025 was 13,455 which is 3% above Q2 2024. Scotland was the only UK nation to see an increase for this period. England, Northern Ireland and Wales all saw decreases.
Q2 2025 had the second highest number of reported private admissions ever. The only higher quarter was Q1 2025. This was the first time since 2019 that a Q2 figure did not exceed the Q1 figure.
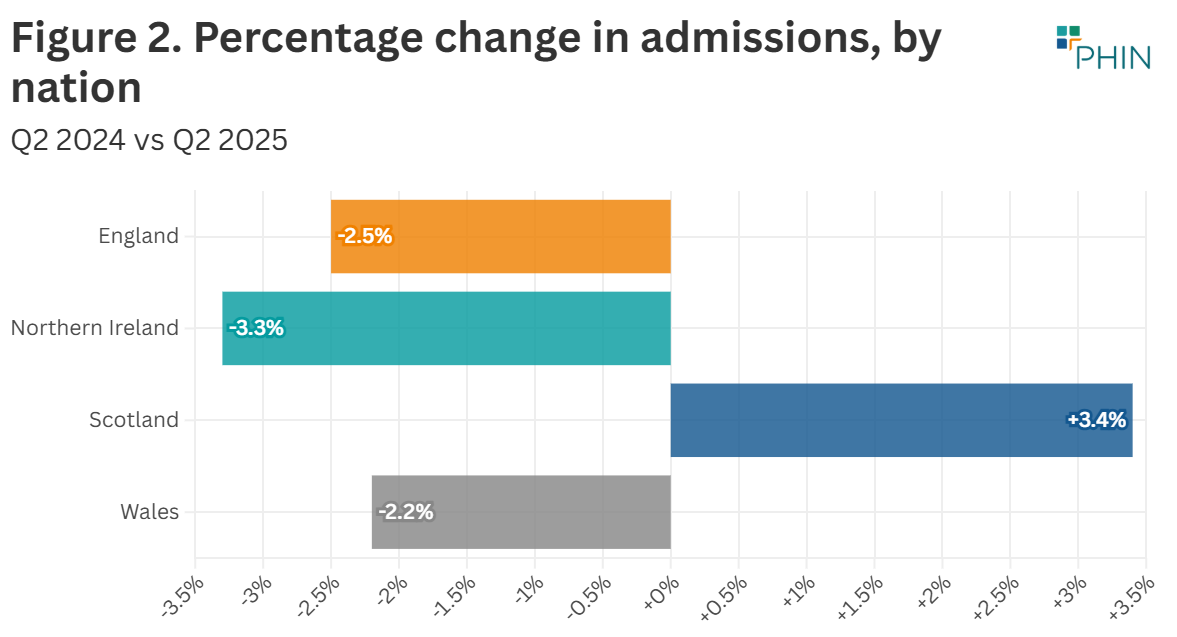
Both private medical insurance funded admissions and self-pay increase
Insured admissions
Reported admissions paid for with private medical insurance in Q2 2025 (7,290) rose by 3% compared to the same period in 2024.
In contrast, insured admissions fell in Northern Ireland and every English region except one.
Self-pay admissions
Self-pay admissions in Scotland (6,165) in Q2 2025 were up 4% compared to Q2 2024.
Across the UK, self-pay was down in Wales and across all but three of the English regions.
Table 1. Q2 admissions by payment method (rounded figures)
| Year | Insured | Self-pay |
|---|---|---|
| Q2 2023 | 6,280 | 5,670 |
| Q2 2024 | 7,060 | 5,955 |
| Q2 2025 | 7,290 | 6,165 |
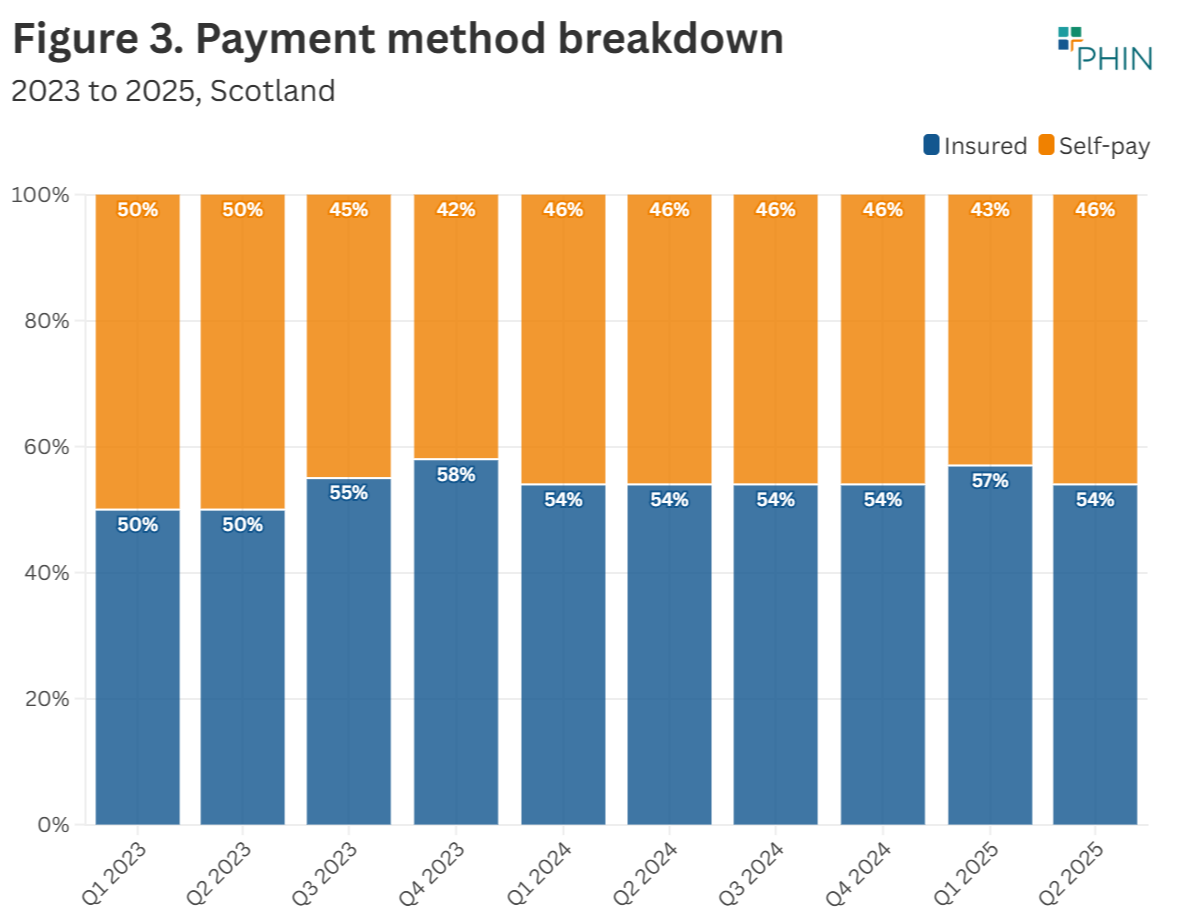
The proportion of admissions paid for using each funding method was the same as in Q2 2024.
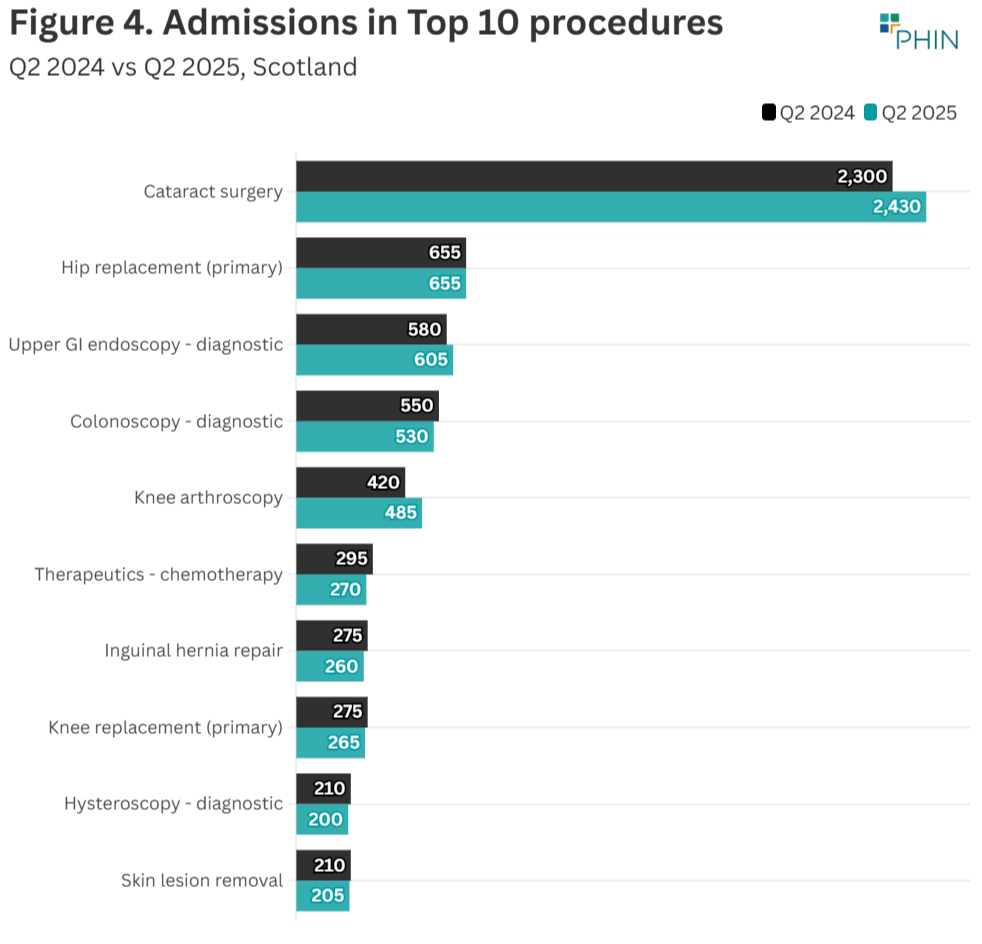
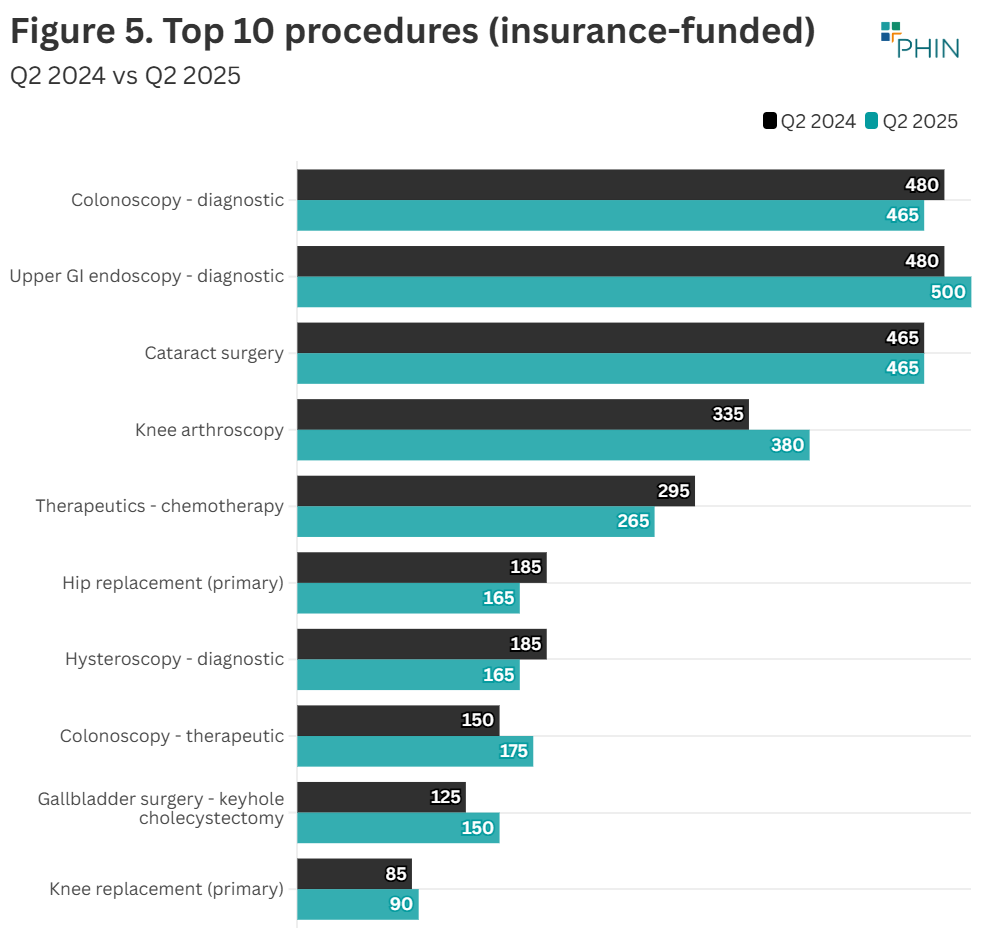
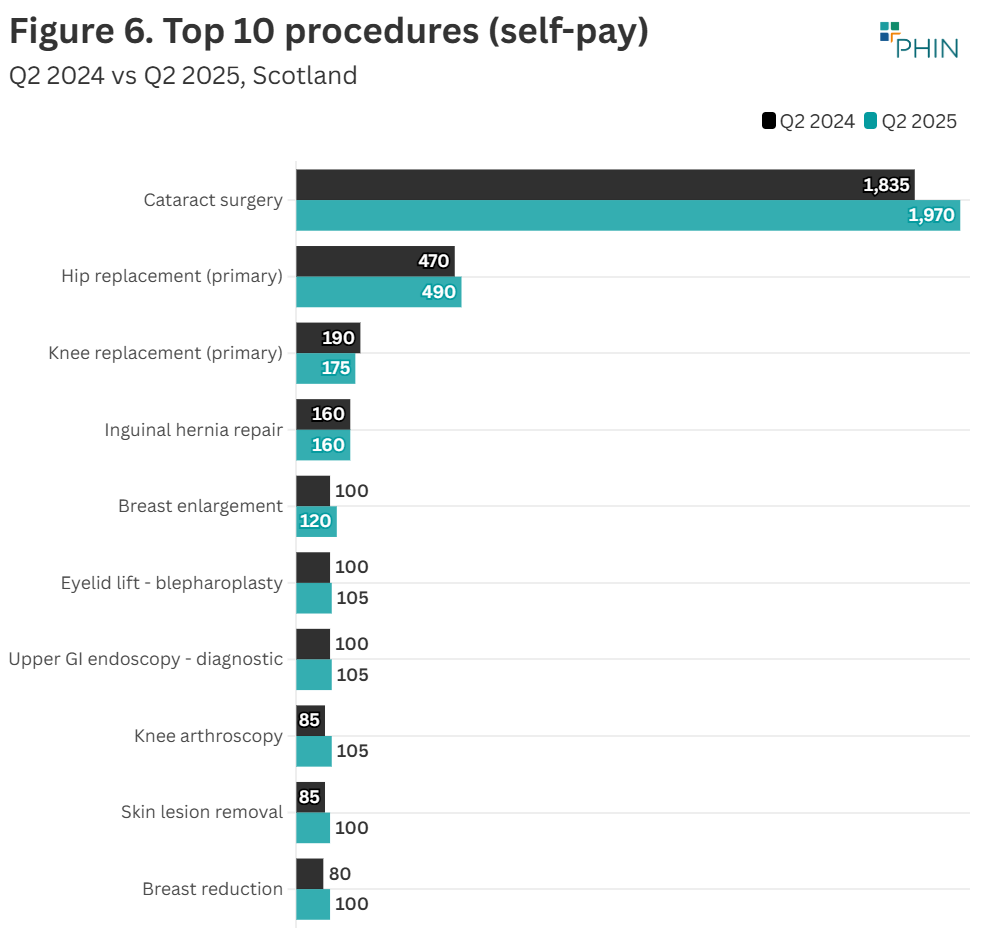
Top 10 procedures
There was an increase in admissions for four of the Top 10 procedures by volume when comparing Q2 2025 to Q2 2024.
‘Cataract surgery’ (2,430 admissions) is the largest procedure by volume, and increased by 130 (6%). ‘Hip replacement’ (655) is the second highest and remained at the same level. ‘Colonoscopy - therapeutic’ had the largest percentage increase (22%), but is a less common procedure (225).
The Top 3 procedures by Q2 volume are:
- ‘Cataract surgery’ (2,430)
- ‘Hip replacement’ (655)
- ‘Upper GI endoscopy - diagnostic’ (605)
Active consultants in private healthcare
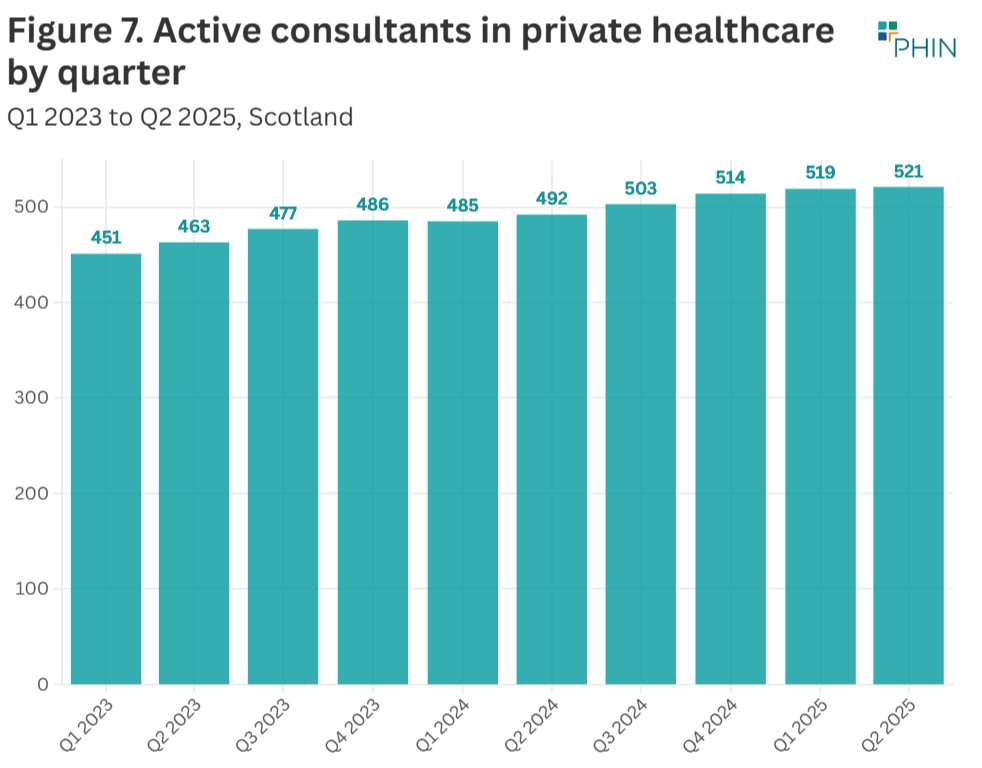
The number of consultants active in private healthcare regularly fluctuates as new consultants start working in the private sector, and existing ones go on sabbatical, stop practising privately, or retire.
In Q2 2025, there were 29 more active consultants than in Q2 2024.
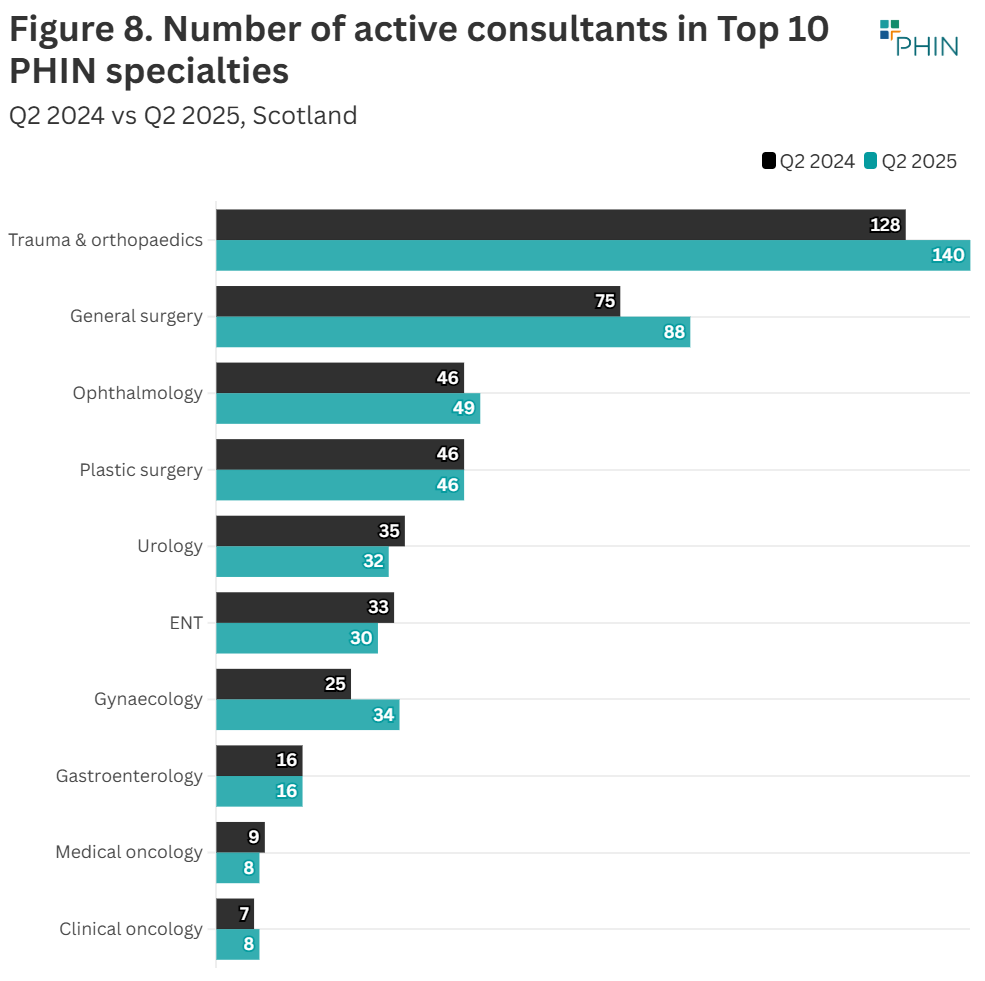
‘General Surgery’ had the largest volume (13 extra consultants) increase in active consultants in the top 10 procedure groups in Q2 2025. Gynaecology had the largest percentage increase (36%).
‘Urology’ saw the largest decline by volume (3), while ‘Medical oncology’ had the biggest percentage decrease (11%), though this was only a reduction of one consultant.
Patient demographics
Female insured admissions increased by 3%, and male insured admissions increased by 4%. The gap between the sexes is now fewer than 200 admissions.
Self-pay funded admissions increased by 1% for female admissions and 3% for male admissions. There were around 1,000 more admissions for female patients using this payment method.
Table 3. Volume of admissions by sex and payment method
| Sex | Admissions Q2 2024 | Admissions Q2 2025 | Funding type | Comparison Change % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 3,635 | 3,735 | Insured | 3% |
| Female | 3,475 | 3,515 | Self-pay | 1% |
| Male | 3,420 | 3,550 | Insured | 4% |
| Male | 2,475 | 2,560 | Self-pay | 3% |
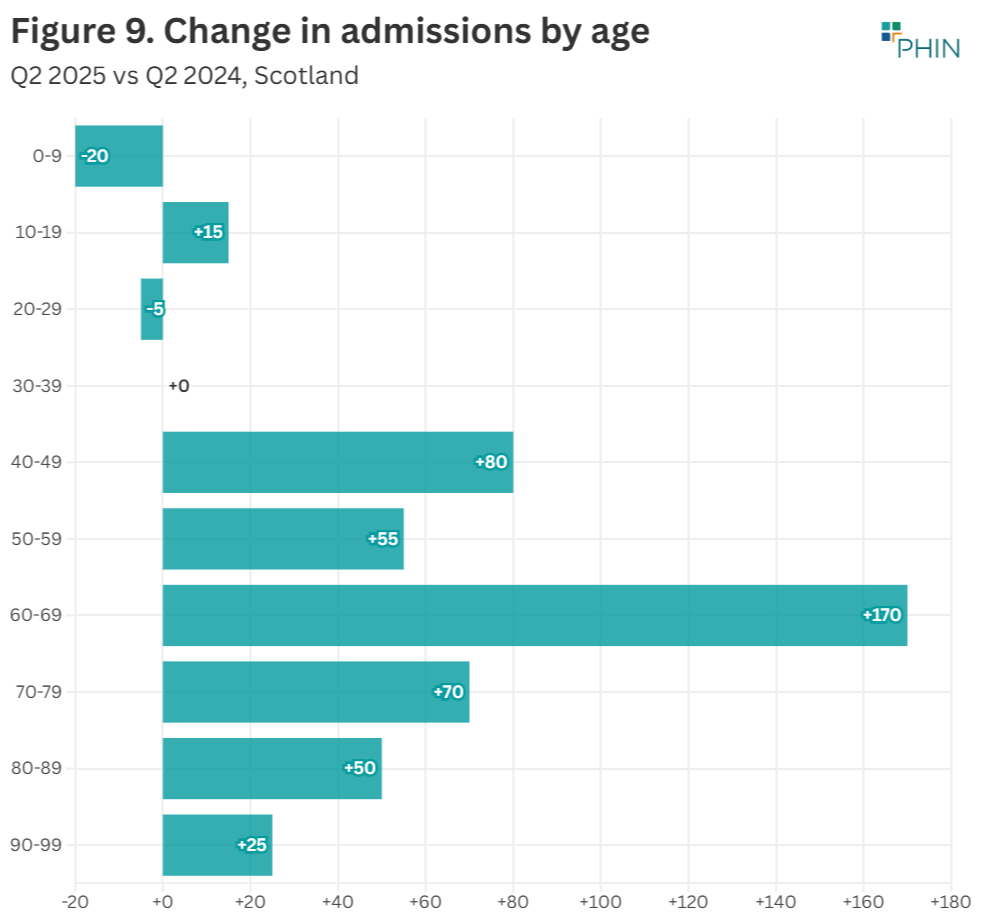
There was an increase in admissions in all age groups except for the 0-9 and 20-29 year olds in Q2 2025 compared to the same quarter in 2024. Of those groups, the largest volume (20) and percentage decrease (17%) was for the 0-9 year olds.
Conversely, the largest volume increase (170) was in the 60-69 group and percentage increase (26%) was in the 90-99 age group.
Important notes (updated)
All data described above is taken from PHIN’s unique, national private dataset describing discharge activity (day case and inpatient). This excludes activity outside of PHIN’s mandate from the Competition and Markets Authority , such as outpatient diagnostics, physiotherapy and mental health services.
There is a time lag between collecting, validating and processing the data we receive from hospitals before we can publish it. This can be up to six months after treatment has been completed, to ensure a fair process and accurate data.
Occasionally, hospitals may submit data after our deadline. This will not be included in the current quarter’s Market Update, but will be added to future ones. For this reason, we always recommend only using figures from the latest Update as they can change.
For ease of use, we have reduced the number of years of data shown in the Market Update. If you would like to access pre-2023 data, please get in touch.
Activity numbers have been rounded to the nearest five, with percentages based on the unrounded figures.
